Richard Sharpe Shaver, born 1907 in Berwick, Pennsylvania, became a national sensation in the forties with his dramatic accounts of a highly advanced civilization that inhabited Earth in prehistoric times. An itinerant Midwesterner, he’d been employed as a landscape gardener, a figure model for art classes, and a welder at Henry Ford’s original auto plant. He gained public attention as a writer who asserted that descendants of those early beings still live in hidden underground cities, where they wield terrifying technology capable of controlling thoughts. Many readers agreed with Shaver, and a splashy controversy ensued.
Public fascination with his writings subsided during the fifties, but Shaver continued searching for evidence of a great bygone civilization. In about 1960, while living in rural Wisconsin, Shaver formulated a hypothesis that would captivate him for the balance of his life: some stones are ancient books, designed and fabricated by people of the remote past using technology that surpasses anything known today. He identified complex pictorial content in these “rock books.” Images reveal themselves at every angle and every level of magnification and are layered throughout each rock. Graphic symbols and lettering also appear in what he called “the most fascinating exhibition of virtuosity in art existent on earth.”
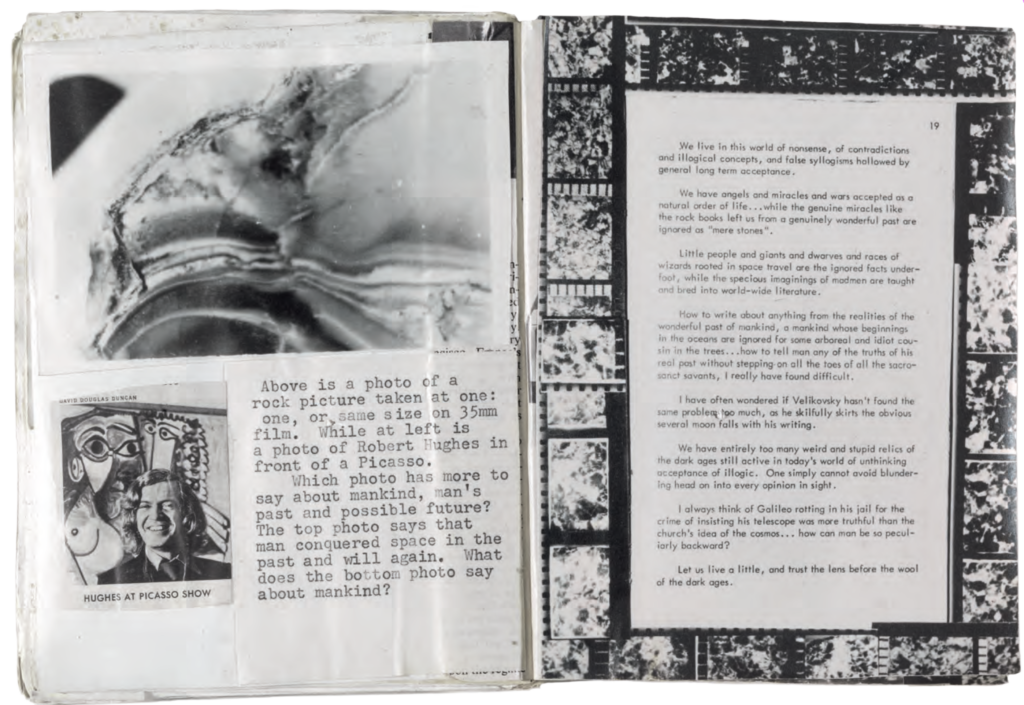
Frustrated that the equipment needed to fully decipher the dense rock books was lost to time, Shaver undertook strategies to make at least a fraction of the books’ content clearly visible. Initially, he made drawings and paintings of images he found in the rocks, developing idiosyncratic techniques to project a slice of rock onto cardboard or a wooden plank. Shaver also produced conventional black-and-white photos using 35 mm film, often showing a cross section of rock alongside a ruler or a coin to indicate scale. Sometimes he highlighted imagery by hand coloring the prints with felt pens. He attached photos to typewriter paper where he added commentary: he describes the rock books, interprets images, details his photo techniques, and expresses disappointment at the conspicuous lack of academic or journalistic interest in his findings.
Shaver and his wife, Dorothy, moved in 1963 to Summit, Arkansas, where he established his Rock House Studio on their small property. There, in addition to painting, he processed and printed film. His efforts at illuminating the rock books moved away from painting and toward photography in his final years. That shift may have been influenced by his perception that viewers interpreted the paintings as a product of his imagination rather than an objective record of ancient artifacts. Shaver wrote, “People will believe photos and won’t believe drawings or paintings… the camera wins, by being honest. Which doesn’t say much for artist’s honesty, I guess. We try… but people think we lie.”
Shaver made small books on paper at his studio—some illustrated with his drawings or collages of rock photos—which he produced with a local printer. He kept his manuscripts in file folders with colorful hand-lettered titles. As many as twenty booklets were planned; five of them, plus a brochure about “pre-deluge art stones,” are known to have seen print. Each one views the prehistoric library in stone from a different angle. “Giant Evening Wings” is named after swarming ape-bats that threatened the ancient Amazons; “Blue Mansions” features the undersea Mer people; “The Vermin from Space!!!” paints a bleak picture involving rock books, mind control, and flying saucer sightings: “We are a remnant of an ancient race, adrift on a dying world and the parasites of space circle us, looking for a place to sink in their sucking tube.”